Introduction to Respiration in Plants
Introduction to Respiration in Plants: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Respiratory Substrates, Respiration in Plants, Exchange of Gases in Plants, Cellular Respiration, Aerobic Respiration, Anaerobic Respiration, Site of Cellular Respiration, ATP Synthase in Mitochondria, etc.
Important Questions on Introduction to Respiration in Plants
Study the given figure and select the incorrect option regarding this.
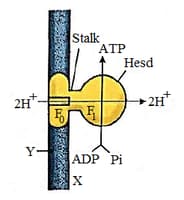
How many ATP are produced when a NADH molecule is oxidised?
NADH is an example of energy-carrying molecule.
Name the energy carrying molecule synthesised by the complex V located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. (Answer the acronym form)
Which of the following molecule synthesised in the mitochondria is referred to as the energy currency of the cell?
Define energy carrying molecule. Give one example of energy carrying molecule.
Which part of the cellular respiration utilises the created FADH2 molecules?
There are 3 ATP molecules produced from the oxidation of one molecule of FADH2.
How many ATP molecules are produced after the oxidation of one molecule of FADH2?
Which of the following process indicates oxidative process?
Pyruvate can be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide by Yeast.
38 ATPs are formed in fermentation.
In ATP molecule, the type of sugar present is ribose or deoxyribose. (Answer from the bold words)
In glycolysis, the net gain of ATP from one molecule of glucose is (Write on words)
Arrange the following steps in ascending order based on no. of molecules gained when one glucose molecule participate in aerobic respiration.
I) Total no. of in Krebs cycle
II) Succinyl COA Succinic acid
III) Pyruvic acid Acetyl
IV)
Choose the correct combination.
| Enzyme Reaction | Enzyme Name | Enzyme Class | |
| A | Glutamic acid Glutamine | Glutamate synthase | Ligase |
| B | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate Fructose-6-monophosphate. | Phosphatase | Hydrolase |
| C | Glucose Glucose-6-phosphate | Hexokinase | Transferase |
| D | Argininosucci acid Arginine | Arginosuccinase | Lyase |
Assetion (A): In muscle cells, when is inadequate for cellular respiration, lactic acid is produced. In yeast, pyruvic acid is converted to and ethanol.
Reason (R): Yeast cells will die by the concentration of of alcohol.
The correct option among the following is
The number of glucose molecules required to produce molecules under anaerobic conditions by yeast cell is
_____, carbon dioxide and a little amount of energy are produced during anaerobic respiration. (Write the name)
Aerobic respiration occurs in all except
